Lesson 4: OCI Storage Services
Overview

Block Storage
Like a hard drive in a server except the hard drive happens to be installed in a remote chassis. 如同服务器中的硬盘驱动器,但硬盘驱动器恰好安装在远程机箱中
Data is typically stored on device in fixed sized blocks (e.g 512 Bytes).
Accessed by operating system as mounted drive volume. Block storage 通过操作系统作为已安装的驱动器卷进行访问
Applications/file systems decide how blocks are combined and accessed.
Data is stored without any higher-level metadata e.g for data format, type or ownership. 数据存储时没有任何更高级别的元数据,例如数据格式,类型或所有权
You can place any kind of file system on block level storage. E.g Windows uses NTFS; VMware uses VMFS.
Block Volume Service
Storage for compute instances (REMOTE)
2 types of Block volumes:
Boot Volume (OS disk)
Block Volume (data disks)
Why do we use Block Volume: it lets you store data independently and beyond the lifespan of compute instances. 它使可以独立存储数据和独立于实例的使用寿命
When instance dies, Your boot volume and your data volumes are all still available. So Block Volume is used for data durability 数据持久化.
Block Volume Use ases
Databases
Exchange (supports block level storage only)
VMware (VMFS volumes on block level storage)
Server boot (in public clouds, instances are configured to boot from block level storage)

Block Volume Highly durable
Storage is highly durable and persistent
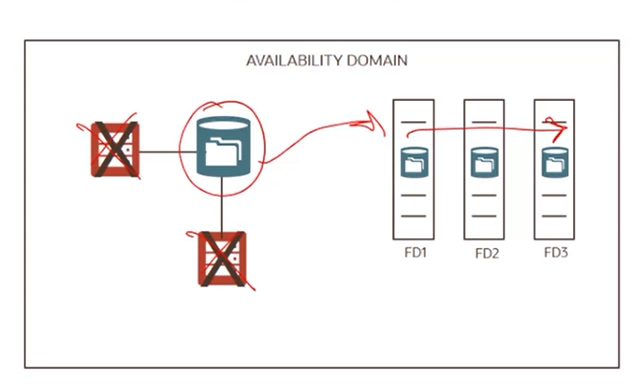
Block Volume store replica of data in 3 separate FDs
You don't need to configure any software based protection (RAID 10 etc)
A backup is recommend for minimize losing data.

Block Volume Backup
Complete point-in-time snapshot copy of your block volumes
Encrypted and stored in the Object Storage, and can be restored as new volumes to any AD within the same region
Can copy block volume backups from one-region to another
Backups can be scheduled
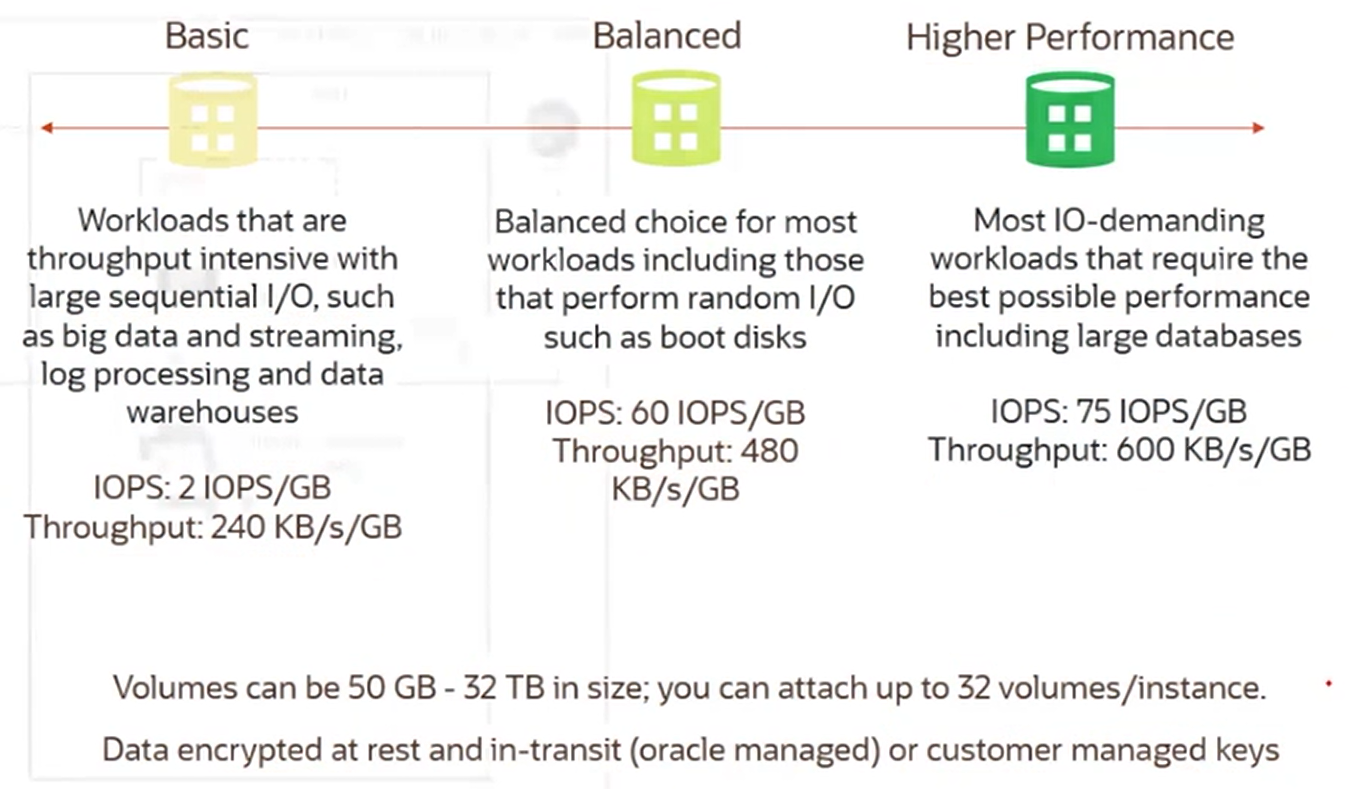
Block Volume Tiers
Local NVMe
Temporary storage locally attached directly to the compute instances
high-performance local storage
Storage is non-persistent (survives reboot)
Local NVMe Use cases
NoSQL DB
in-memory DB
On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP, 在线交易处理)
Scale-out transnational DB
Data warehousing (数据仓库)
File Storage
Hierarchical collection of documents
Distributed files standards
NFS
SMB
File Storage Service (FSS)
Shared file system storage for compute instances
Support NFSv.3 distributed fils system
Data protection: Snapshots
Security: data-at-rest and in-transit encryption for all file systems & metadata
File Storage Highly durable
Highly durable and Persistent
File storage stores replica of data in 3 separate FDs
File Storage Uses cases
Oracle Applications
HPC
Big Data and Analytics
General purpose File systems (e.g. NAS)
Object Storage
All data is managed as objects, for storing unlimited of unstructured data.
Each object is composed of object itself and object's metadata
Each object is stored in a bucket1, this means that accessing individual objects is fast and easy.
Without a folder hierarchy
High scalability and reliability
Object storage relies on standard HTTP verbs (GET, PUT, POST, UPDATE, DELETE )
Object Storage Service
Regional service, not tied to any specific compute instance
Offers 2 distinct storage classes
Hot Storage
Cold Storage
Object Storage Tiers
1. Standard Storage Tier (Hot)
Fast, immediate and frequent access.
Data retrieval is instantaneous. 数据检索是即时的
Always serves the most recent copy of data when retrieved. 检索时始终提供最新的数据副本
Standard buckets can't be downgraded to archive storage. 无法将标准存储桶降级到归档存储
2. Archive Storage Tier (Cold)
Rarely accessed data, must be retained and saved for long period of time.
10 times cheaper than Standard Storage Tier
90 days minimum for storage
Objects need to be stored before download; Time To First Byte (TTFB) after restore request is made: 4 hours
Archive buckets can't be downgraded to standard storage
Object Storage Highly durable
Highly durable and Persistent
File storage stores replica of data in 3 separate FDs
In a multi-AD region, it stores replica of data in more than on AD
Data detected and auto repaired
For disaster recovery
Object Storage Use cases
Content repository for data, images, logs and video etc.
Archive/ Backup for longer periods of time.
Storing log data for analysis and debugs/ troubleshooting.
Storing large data sets (genome data, IoT).
Big data, Hadoop
1 bucket: is a logical container for storing objects
最后更新于