Lesson 3: OCI Compute Services
Bare Metal 裸机
A physical server without any virtualization, you have to set up a virtualization layer, then you have to manage all the things: OS, run-times etc. Oracle offer a off-box virtualization1
Uses cases
Direct Hardware Access with all the Security, Capabilities, Elasticity and Scalability of OCI.
Workloads that are performance-intensive
性能密集型工作负载
Workloads that are not virtualized
Workloads that require a specific hypervisor
Workloads that require BYOL (Bring Your Own Licensing)
Dedicated Virtual Hosts 专用虚拟主机
A host server, It has a virtualization, you can run VMs on top of that.
Virtual Machines
A virtual machine is a guest on a host server with hypervisor based virtualization.
Use cases
VMs require work - OS path management, security configuration, monitoring, application configuration and scaling to handle variable traffic, if you want to:
control all aspects of an environment
deploy a legacy app running on Windows or Linux
move applications from on-premises to OCI
Container Engine
you are managing your code, and then of course you are managing your App container2.
Functions
Oracle Functions where you just write the code. You write the code in different languages, and you don't worry about any of the underlying infrastructure.
small but powerful blocks of code
stored as Docker images in a specified Docker registry.
invoked in response to a CLI command or signed HTTP request (为了响应CLI命令或签名的HTTP请求而调用)
Instance basics
Compute instances depend on other OCI services such as Block Volume and Virtual Cloud Network (VCN)

Vertical Scaling
Scale-up and Scale-down instance shape (实例外形) supported, the instance must be stopped before resize it.
Autoscaling
Which is literally horizontal scaling. Enables large scale deployment of VMs from a single gold image with automatic configuration, referred to as Scale-out or Scale-in.

How to autoscaling

You have an instance running --> what you do is create a configuration. The configuration is nothing but an operating system image, your metadata, storage disks, all that stuff. It basically earns about what you instance looks like. You're creating this thing called a gold image here.
The take this configuration and you create what is called an instance pool and as you can see here, instead of one instance, now we have two. And you could do many more.
Put these instances in different ADs. Then define your scaling rules to manage hundreds of VMs together as one unit.
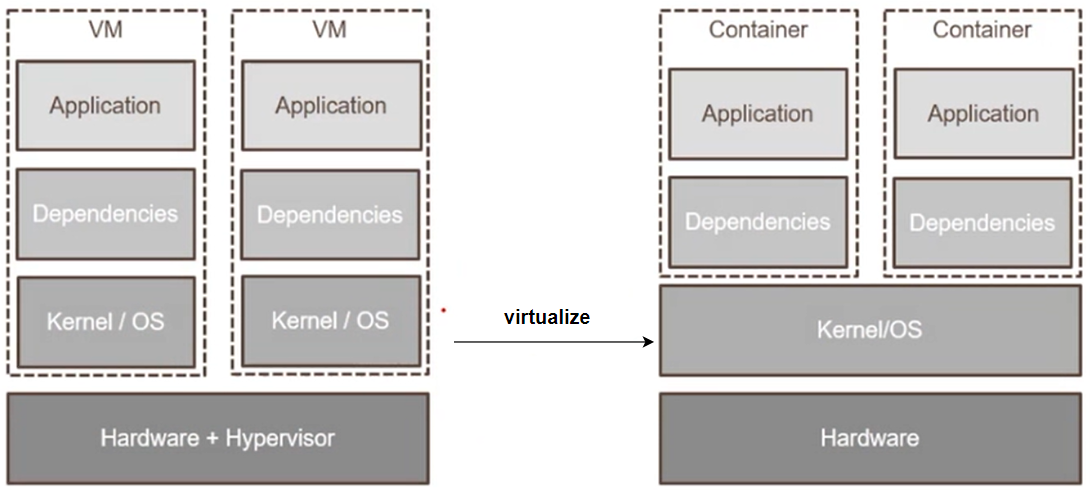
VM vs Container
There were some downsides to VM, you were repeating the operating system everywhere. And so these became bulky (笨重的). For example if you have 10 VMs, basically you're packaging the operating system 10 times.
The concept of containers where we raised the abstraction one more level, and now we abstract/virtualize the operating system. It shares the kernel or the operating system with other containers.
1: off-box virtualization: we off-load network and storage to a separate hardware card in the server. People also call it as custom silicon. 我们把网络和储存卸货到一个单独的硬件卡上.
2 : App container: is a container runtime which executes container and manages container images on a node. The most widely, known app container or container runtime is Docker.
最后更新于